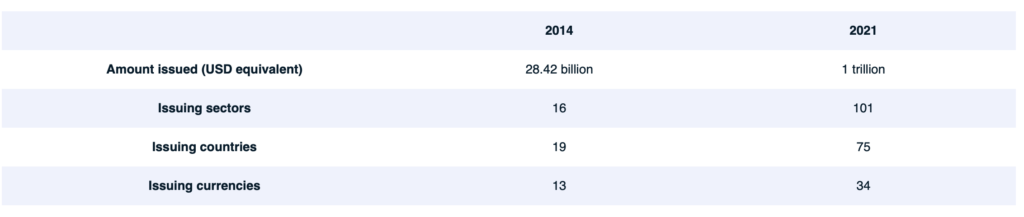
When the International Capital Market Association (ICMA) first published the Green Bond Principles in 2014, the market for self-labeled ESG bonds was small and homogeneous: the equivalent of approximately USD 28 billion in total amount issued, with a large majority (96%) of these bonds self-labeled as “green” bonds.1 Seven years later, the market has grown 25 times, with more than USD 1 trillion in total amount issued in 2021 and a greater distribution of bonds by industry and location of issuer, as well as numerous standards and frameworks applied.
- Growth in regional footprint: From 19 countries issuing bonds in 13 currencies in 2014, the market for self-labeled ESG bonds expanded to 75 countries issuing bonds in 34 different currencies in 2021.1 This growth in issuance and size coincided with a more complicated set of objectives and definitions governing the numerous self-labeled ESG bonds.
- Growth in sector and industry footprint: In 2021, self-labeled ESG-bond issuance spanned 101 company types, including apparel retailers, charity organizations, food processors and gold miners. This represents substantial growth from 2014, when only three or four primary company types (i.e., financial institutions, supranationals, utilities and agencies) issued ESG bonds.2
- Growth in frameworks and taxonomies: ICMA’s 2014 Green Bond Principles were followed by several green-bond standards (GBS) and methodologies — including GBS proposed by the European Union and Association of Southeast Asian Nations; the Climate Bonds Standard from the Climate Bonds Initiative; and guidelines for green-bond issuance from India, China, Brazil and other national governments. Seventeen countries, including Canada, China, Russia and the Philippines, have developed region-specific green taxonomies — either voluntary or mandatory — for classifying green activities; seven more countries are developing their own green taxonomies. In the EU, the EU Taxonomy for Sustainable Activities sets the definition of green activities for financing for all EU member states.
Growth in issuance of ESG-labeled bonds
Growth in issuance of ESG-labeled bonds by type
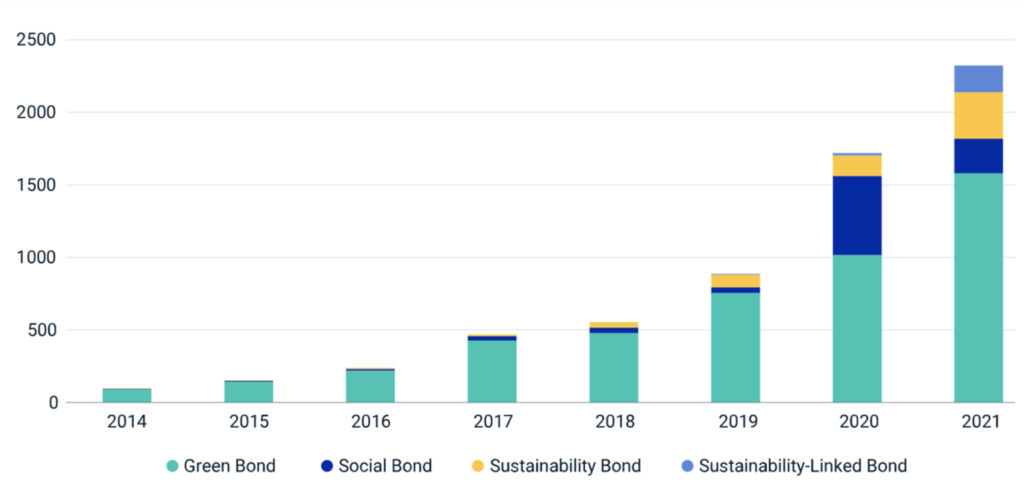
ESG-labeled bonds not only grew as a market in the years since 2014; they became increasingly complex, as their objectives broadened beyond environmental ones alone. To introduce standards and transparency to this more complex ESG-bond market, ICMA released the Social Bond Principles and Sustainability Bond Guidelines in 2017 and Sustainability-Linked Bond Principles in 2020. These principles and guidelines have become the market standard used by issuers to self-label their bonds.
In 2021, self-labeled ESG bonds were issued across four broad categories (green, social, sustainability and sustainability-linked) with a combined market value of USD 1 trillion. After green bonds dominated the ESG-bond market from 2014 to 2018, social bonds increased as a share of the market — an issuance trend that accelerated in 2020 with a rush to address the economic ills caused by COVID-19. During 2020, the growth of social-bond issuance was even greater than that of green bonds. In 2021, there were also increases in the issuance of sustainability bonds, a combination of green and social use of proceeds, and of sustainability-linked bonds — which are very different in their aim and structure from green, social and sustainability bonds, as they do not ring-fence proceeds, but rather tie the bonds’ coupon to the sustainability performance of the issuer.
Categories of ESG-labeled bonds
Within these already diverse categories, more narrowly defined thematic bonds continue to emerge. Given the vast market and types of bonds issued, we provide an overview of the main categories of ESG bonds below, with a focus on how issuers use the proceeds:
- Green bonds: Proceeds raised from a green bond are used toward projects and activities promoting a broad range of environmental objectives.
Estimated amount issued in 2021: USD 516 billion equivalent
Largest issuers in 2021:- U.K. — USD 21.9 billion equivalent
- KfW Bankengruppe — USD 19.3 billion equivalent
- Italy — USD 16.1 billion equivalentIssuers by type:
- Sovereign/agency/supranational — 13%
- Corporate — 87%3Within the broader green-bond category, there are a range of thematic bonds with a specific, narrowly defined use of proceeds. A few examples:
- Climate bonds: Proceeds target climate-change solutions such as mitigation- or adaptation-related projects and activities.
- Blue bonds: Proceeds target projects in the “blue economy” — for example, development of marine energy or sustainable fisheries.4
- Transition bonds: Proceeds are for transition to cleaner fuels or energy sources, although not for zero-emission fuels.
- Social bonds: Proceeds are used to fund projects or activities addressing or mitigating a specific social issue, with a goal of achieving positive social impact.
Estimated amount issued in 2021: USD 212 billion equivalent
Largest issuers in 2021:- European Union — USD 60.4 billion equivalent
- Caisse D’Amortissement de la Dette Sociale (CADES) — USD 43.1 billion equivalent
- Chile — USD 13.6 billion equivalentIssuers by type:
- Sovereign/agency/supranational — 47%
- Corporate — 53%5Similar to green bonds, social bonds are often issued to address very specific and narrowly defined objectives. These include:
- COVID-response bonds: Issuance started in 2020 with proceeds used to strengthen health-care infrastructure and alleviate the economic losses caused by the pandemic.
- Affordable-housing bonds: Proceeds target increasing access to affordable housing in the bond’s coverage region.
- Sustainability bonds: Green and social objectives are typically combined in sustainability bonds, with the proceeds going to projects or activities with either positive environmental or social impact, or both.
Estimated amount issued in 2021: USD 183 billion equivalent
Largest issuers in 2021:- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — USD 30.9 billion equivalent
- Inter-American Development Bank — USD 9.1 billion equivalent
- International Development Association — USD 8.7 billion equivalentIssuers by type:
- Sovereign/agency/supranational — 28%
- Corporate — 72%6Sustainability bonds are differentiated from their ESG-bond counterparts by their combination of social and environmental objectives: e.g., clean energy that is also affordable; or applying social criteria, such as do no harm, to the bond’s primary environmental objective; or funding both green and social projects. Within the sustainability themes, bonds may be positioned as Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) bonds. These fund projects that contribute to one or more of the goals set by the SDGs.
- Sustainability-linked bonds: Unlike the use of proceeds for green, social and sustainability bonds, proceeds raised from sustainability-linked bonds are used for general purposes. The coupon of sustainability-linked bonds is tied to the achievement of sustainability targets and failing to achieve them means the issuer is liable for an additional, pre-disclosed interest rate paid to the investors. Increasing numbers of issuers are looking to offer sustainability-linked bonds because their proceeds are not tied to specific projects. This enables companies with traditionally high environmental impact (e.g., cement manufacturers) to issue ESG-labeled debt as an incentive for improving the ESG characteristics of their operations.
Estimated amount issued in 2021: USD 91.5 billion equivalent
Largest issuers in 2021:- ENEL Finance International NV — USD 12.1 billion equivalent
- Teva Pharmaceutical Finance Netherlands II BV — USD 5 billion equivalent
- ASTM SpA — USD 3.4 billion equivalentIssuers by type:
- Corporate — 100%7